A*算法
A* 算法的最大时间消耗在于将节点插入open_set,因此为了最大限度的提升效率,我们的优化方向有两个,一个是优化open_set的数据结构,而另外一个就是尽可能的减少在寻路过程中加入到open_set中的点。
因此可行的解决的方式有:
open_set数据结构的优化可以使用优先队列实现,如下面示例代码所示。优先队列底层的实现逻辑是二叉堆,因此时间复杂度是O(log(n))。-
判断是否将点插入
open_set的依据是F值,而如果在寻路的过程中,如果两点中间存在大阻挡,将会使得将很多无用的点塞入open_set中,因此常见的一种做法是进行分块处理,在可绕过阻挡块处设置寻路点,这样就可以减少要搜索的点。以下图为例,不同块之间除了黑点之外都是阻挡(黑点是桥梁),因此可以把黑点直接设置为寻路点,这样
A -> C,只要分成三个 A* 寻路即可,避免了“撞墙”,大大提升了效率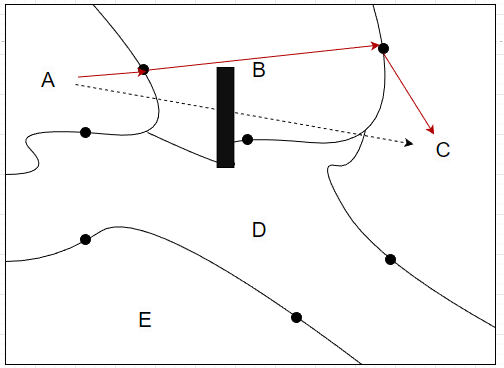
如果图形是没有阻挡的,实际上使用分块的方式依然可以提升整体的性能,所以还是有必要提前划分某些寻路点。 当然要注意,这种分块的形式,得到的一般是一个近似的最短路径,在实际项目工程中也是可以接受的
- 第三种方式就是使用更快的寻路方式了,可以使用
JPS寻路算法
Python版本:
import math
import heapq
# f = g + h
class Node():
Weight = 10 # 这里的权重可以根据不同的地形修改,比如沙漠,那么值应该大些,平原值可以小些
D = 10
DD = 14
def __init__(self, x, y, g=0, h=0):
self.x = x # 坐标x
self.y = y # 坐标y
self.g = g # 当前点到起始点的代价,dijkstra算法
self.h = h # 当前点到终点的代价,最佳优先搜索算法
self.father = None
def calAddG(self, current_node):
if abs(self.x - current_node.x) == 1 and abs(self.y - current_node.y) == 1:
return DD * Node.Weight # 斜线距离,代价为14
else:
return D * Node.Weight # 直线距离,代价为10
def setG(self, val):
self.g = val
def calH(self, node): # 曼哈顿距离,也可以使用欧氏距离
dx = abs(self.x - node.x)
dy = abs(self.y - node.y)
# H的计算主要有三种
# 1. 曼哈顿距离,适用于只有直线的情况下:(dx + dy) * D
# 2. 对角距离:适用于直线+45度角的情况:(dx + dy) + (DD - 2*D) * min(dx, dy)
# 3. 欧几里得距离:适用于任意角度,但是还有sqrt操作,相对较慢
# D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
return D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
def setH(self, val):
self.h = val
def setFather(self, node):
self.father = node
def __lt__(self, other):
return id(self) < id(other)
def __le__(self, other):
return id(self) >= id(other)
class AStar():
def __init__(self, graph):
self.graph = graph
self.max_row = len(graph)
self.max_col = len(graph[0])
def isValid(self, node):
row = node.x
col = node.y
return 0 <= row < self.max_row and 0 <= col < self.max_col and self.graph[row][col] != "#"
def search(self, start_node, end_node):
if not (self.isValid(start_node) and self.isValid(end_node)): # 检查节点的合法性
return []
start_node.calH(end_node)
start_node.setG(0)
path_list = [] # 最后的路径列表
open_list = [] # 当前可选择的点(f, node)
close_list = [] # 已经选择过的点(x,y)
heapq.heappush(open_list, (start_node.g + start_node.h, start_node))
while True:
_val, current_node = heapq.heappop(open_list) # 从优先队列中弹出最小值
close_list.append((current_node.x, current_node.y))
self.searchNear(current_node, end_node, open_list, close_list)
open_node = self.getFromOpenList(end_node, open_list)
if open_node: # 最后的结束节点已在open_list中
while True:
path_list.append((open_node.x, open_node.y))
if open_node.father != None:
open_node = open_node.father
else:
break
elif len(open_list) == 0:
break
return path_list
def searchNear(self, current_node, end_node, open_list, close_list):
"""
搜索节点周围的点
按照八个方位搜索
(x-1,y-1)(x-1,y)(x-1,y+1)
(x ,y-1)(x ,y)(x ,y+1)
(x+1,y-1)(x+1,y)(x+1,y+1)
"""
pos_list = [(-1, -1), (-1, 0), (-1, 1), (0, -1), (0, 1), (1, -1), (1, 0), (1, 1)]
for pos_x, pos_y in pos_list:
self.searchOneNode(current_node, end_node, Node(current_node.x + pos_x, current_node.y + pos_y), close_list,
open_list)
def searchOneNode(self, current_node, end_node, node, close_list, open_list):
"""
搜索一个节点
"""
row = node.x
col = node.y
if self.graph[row][col] == "#": # 是障碍点
return
if (node.x, node.y) in close_list: # 已遍历过
return
open_node = self.getFromOpenList(node, open_list)
tempG = current_node.g + node.calAddG(current_node)
tempH = node.calH(end_node)
if not open_node: # 当前node不在open_list中,计算其G,H存入open_list中
node.setG(tempG)
node.setH(tempH)
node.setFather(current_node)
heapq.heappush(open_list, (node.g + node.h, node))
else:
if (open_node.g > tempG):
# need heapify
open_node.setG(tempG)
open_node.setH(tempH)
open_node.setFather(current_node)
heapq.heapify(open_list) # 重新调整
def getFromOpenList(self, node, open_list): # 如果不在open_list中则返回False,亦可作为判断用
if not open_list:
return None
for _val, open_node in open_list:
if open_node.x == node.x and open_node.y == node.y:
return open_node
return None
if __name__ == '__main__':
graph = [list("####################"),
list("#*****#************#"),
list("#*****#*****#*####*#"),
list("#*########*##******#"),
list("#*****#*****######*#"),
list("#*****#####*#******#"),
list("####**#*****#*######"),
list("#*****#**#**#**#***#"),
list("#**#*****#**#****#*#"),
list("####################")]
print('graph: ')
for g in graph:
print(g)
star = AStar(graph)
path_list = star.search(Node(1, 1), Node(8, 18))
for x, y in path_list:
graph[x][y] = "O"
print('after A* graph: ')
for g in graph:
print(g)
C++版本:
#include <limits.h>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <math.h>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class aStar
{
public:
using Map = vector<vector<int>>;
vector<pair<int, int>> search(const Map&, int, int, int, int);
private:
bool _isValid(const Map&, int, int);
int _calH(int, int, int, int);
int _calG(const Map&, int, int, int);
static const int D = 10; // 直线运动的代价
static const int DD = 14; // 斜线运动的代价
int _maxX; // 当前地图X的最大值
int _maxY; // 当前地图Y的最大值
struct Node
{
int x; // x轴位置
int y; // y轴位置
int g; // g值
int h; // h值
Node* parent; // 父节点
bool close; // 是否已经在close中,true是,false否
Node(int x, int y): x(x), y(y), close(false), parent(nullptr){}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const Node* node1, const Node* node2)
{
return node1->g + node1->h > node2->g + node2->h;
}
};
};
bool aStar::_isValid(const Map& map, int x, int y)
{
return 0 <= x < _maxX && 0 <= y < _maxY && map[x][y] > -1;
}
int aStar::_calH(int current_x, int current_y, int end_x, int end_y)
{
int dx = abs(current_x - end_x);
int dy = abs(current_y - end_y);
/*
三种计算方式:
1. 曼哈顿距离,适合只能直线运动的场景:(dx + dy) * D
2. 对角距离,适合直线+45度角运动的场景:(dx + dy) + (DD - 2*D) * min(dx, dy)
3. 欧几里得距离:适合任意角度运行,有sqrt操作,相对较慢,开方可以使用别的方式优化:D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
*/
return D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
}
int aStar::_calG(const Map& map, int dest_x, int dest_y, int weight)
{
/*
如果是直线运动,则结果会是 D * 目标坐标点的地形权重,比如沙漠权重高点,平地权重就低点,即优先走平地
*/
return weight * map[dest_x][dest_y];
}
vector<pair<int, int>> aStar::search(const Map& map, int start_x, int start_y, int end_x, int end_y)
{
static vector<pair<int, int>> path{
/*
搜索节点周围的点
按照八个方位搜索
(x-1,y-1)(x-1,y)(x-1,y+1)
(x ,y-1)(x ,y)(x ,y+1)
(x+1,y-1)(x+1,y)(x+1,y+1)
*/
{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, -1}, {1, 1} // 前四个方向是直线,后四个是斜线
};
_maxX = map.size();
_maxY = map[0].size();
if (!_isValid(map, start_x, start_y) || !_isValid(map, end_x, end_y)) // 起始/终点坐标异常
{
return {};
}
unordered_map<int, Node*> nodeMap;
Node* startNode = new Node(start_x, start_y);
nodeMap[startNode->x + _maxX * startNode->y] = startNode; // x + maxX * y 这种方式可以保证x和y计算出来的值是唯一的
startNode->g = 0;
startNode->h = _calH(startNode->x, startNode->y, end_x, end_y);
priority_queue<Node*, vector<Node*>, cmp> Que; // 使用 priority_queue 会有重复插入的问题,因此需要使用close字段进行判断,和dijkstra算法处理相似
Que.emplace(startNode);
vector<pair<int, int>> ret;
while (!Que.empty())
{
Node* parentNode = Que.top();
Que.pop();
if (parentNode->close) continue;
parentNode->close = true;
if (parentNode->x == end_x && parentNode->y == end_y)
{
while (parentNode->parent != nullptr)
{
ret.emplace_back(parentNode->x, parentNode->y);
parentNode = parentNode->parent;
}
ret.emplace_back(parentNode->x, parentNode->y);
// 内存释放
for (auto iter = nodeMap.begin(); iter != nodeMap.end(); ++iter) delete iter->second;
return ret;
}
for (int i = 0; i < path.size(); ++i)
{
int new_x = path[i].first + parentNode->x;
int new_y = path[i].second + parentNode->y;
if (!_isValid(map, new_x, new_y)) continue;
int idx = new_x + _maxX * new_y;
if (nodeMap.find(idx) != nodeMap.end()) // 已经遍历过
{
Node* childNode = nodeMap[idx];
if (childNode->close) continue;
int new_g = _calG(map, new_x, new_y, i < 4 ? D : DD); // 直线 or 斜线,对于重复的节点,这里就会由于父节点位置的不同产生不同的值
int new_h = _calH(new_x, new_y, end_x, end_y);
if (new_g + new_h < childNode->g + childNode->h) // 有更小的权重,这里会造成重复插入,上面有过滤,因此无妨
{
childNode->g = new_g;
childNode->h = new_h;
childNode->parent = parentNode;
Que.emplace(childNode);
}
}
else
{
Node* childNode = new Node(new_x, new_y);
nodeMap[idx] = childNode;
int new_g = _calG(map, new_x, new_y, i < 4 ? D : DD); // 直线 or 斜线
int new_h = _calH(new_x, new_y, end_x, end_y);
childNode->g = new_g;
childNode->h = new_h;
childNode->parent = parentNode;
Que.emplace(childNode);
}
}
}
return {}; // 没有找到路径
}
int main()
{
// vector<vector<int>> map{ // -1表示阻挡,其他数值表示当前点的权重值,值越大代表地形越"难走",优先级越低
// {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
// {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
// {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
// {1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ,0, 1, 0 ,0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
// {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
// };
vector<vector<int>> map{ // -1表示阻挡,其他数值表示当前点的权重值,值越大代表地形越"难走",优先级越低
{-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1},
{-1, 0, 5, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1},
{-1, 0, 10, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1},
{-1, 10, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1},
{-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, -1},
{-1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, -1},
{-1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1}
};
aStar a;
auto path = a.search(map, 1, 1, 5, 8);
for (int i = path.size()-1; i >= 0; --i)
{
cout << "(" << path[i].first << ", " << path[i].second << ")";
if (i != 0) cout << " => ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
输出:(1, 1) => (1, 2) => (2, 3) => (2, 4) => (2, 5) => (2, 6) => (2, 7) => (3, 8) => (4, 7) => (5, 8)
*/